Getting Started
This guide will help walk you through the basic setup and use of the Essentia Data Lake Manager.
To learn more about how to create a category, see Category Rules.
Repository setup and management
Video Demo
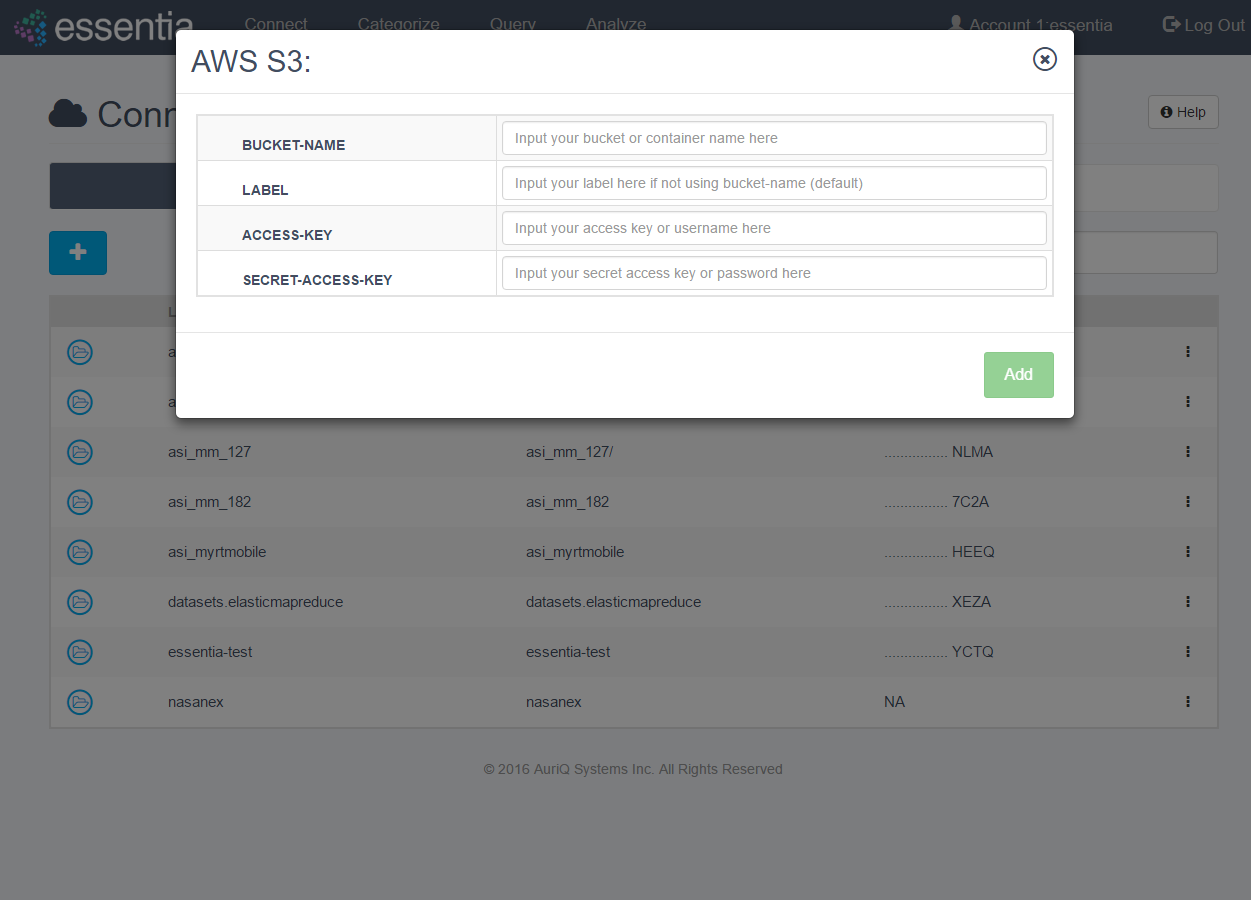
Link to AWS S3
- Click on Connect in the top menu and then the AWS S3 tab.
- Click on the + icon to open the input form.
- Enter your AWS S3 credentials (bucket name, access key, secret access key) and a label if you prefer to call the bucket by another name.
Note: If you are running the AWS Marketplace version of Essentia, you do not need to enter your AWS credentials. Instead, setup an IAM role as described in Authentication.
- Click on the Add button to add your S3 repository.
- Your newly added repository will be displayed in the AWS S3 table.
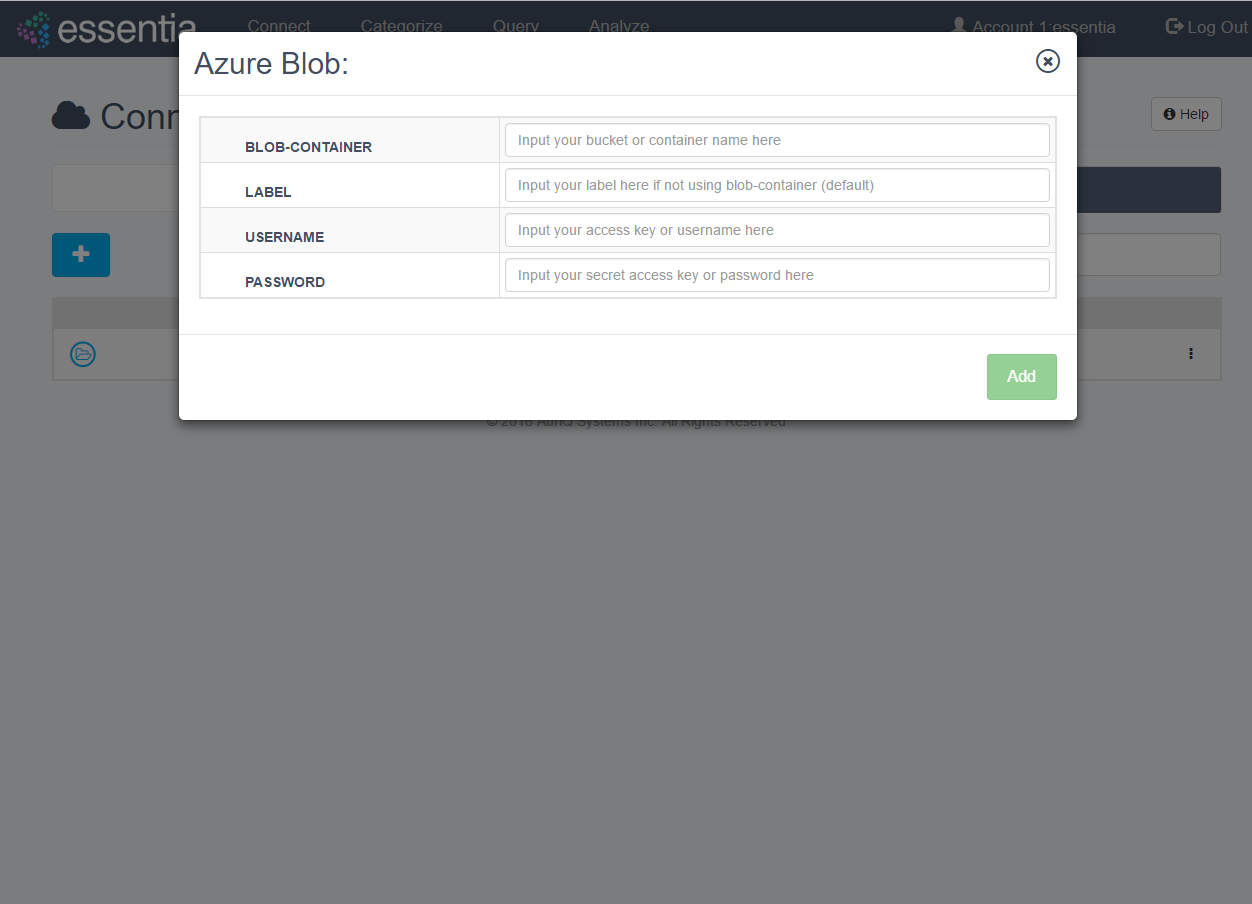
Link to Azure Blob
- Click on Connect in the top menu and then the Azure Blob tab.
- Click on the + icon to open the input form.
- Enter your Azure Blob credentials (container name, username, password) and a label if you prefer to call the container by another name.
- Click on the Add button to add your Blob repository.
- Your newly added repository will be displayed in the Azure Blob table.
Explore Your Data Repository
To explore your new repository or any repository that you’ve already connected to, follow the steps in Exploring Your Data Repository.
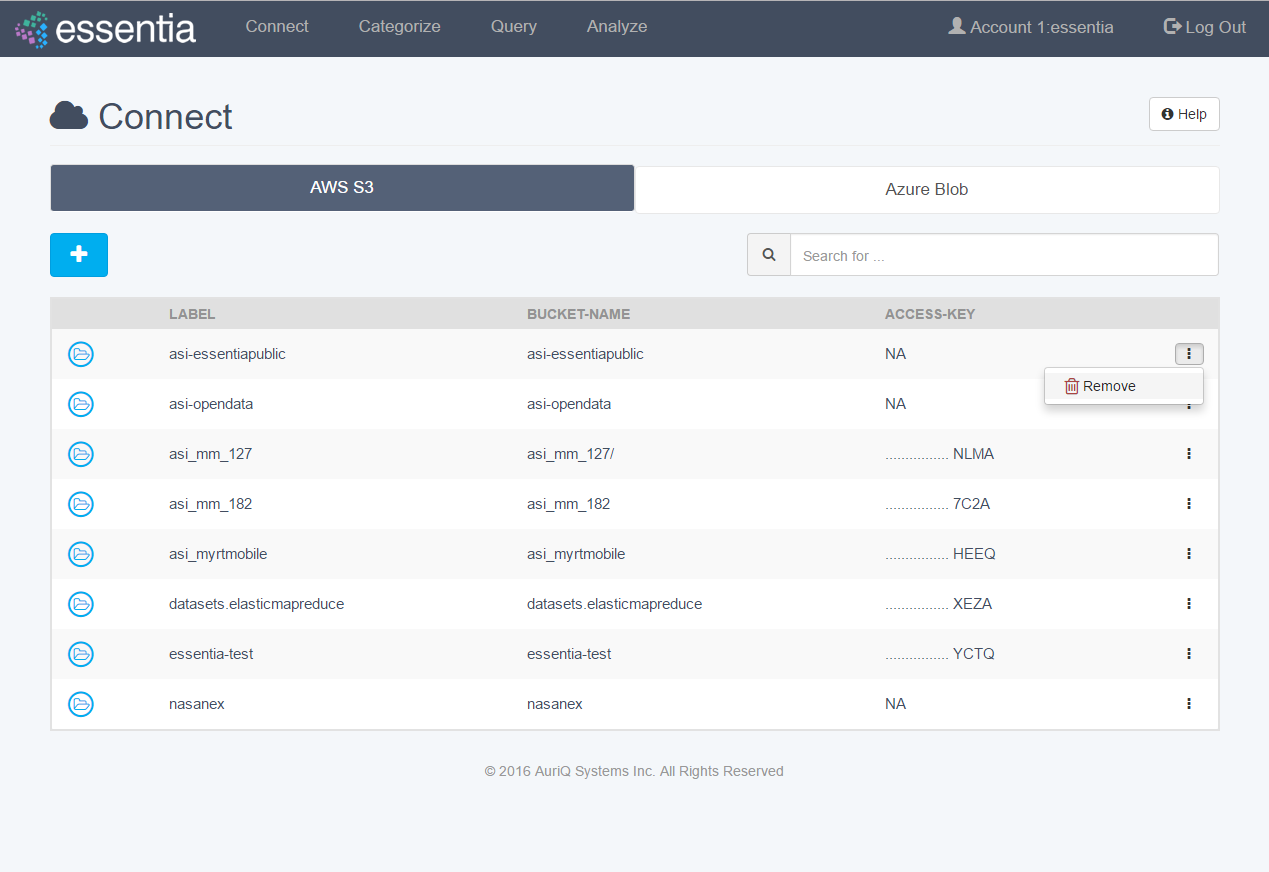
Remove Repository
- Click on Connect in the top menu.
- Choose the appropriate tab (AWS S3 or Azure Blob).
- Click the icon on the right of the table for the repository you want to remove.
- Select the Remove (trash) icon.
- Confirm to delete your setting.
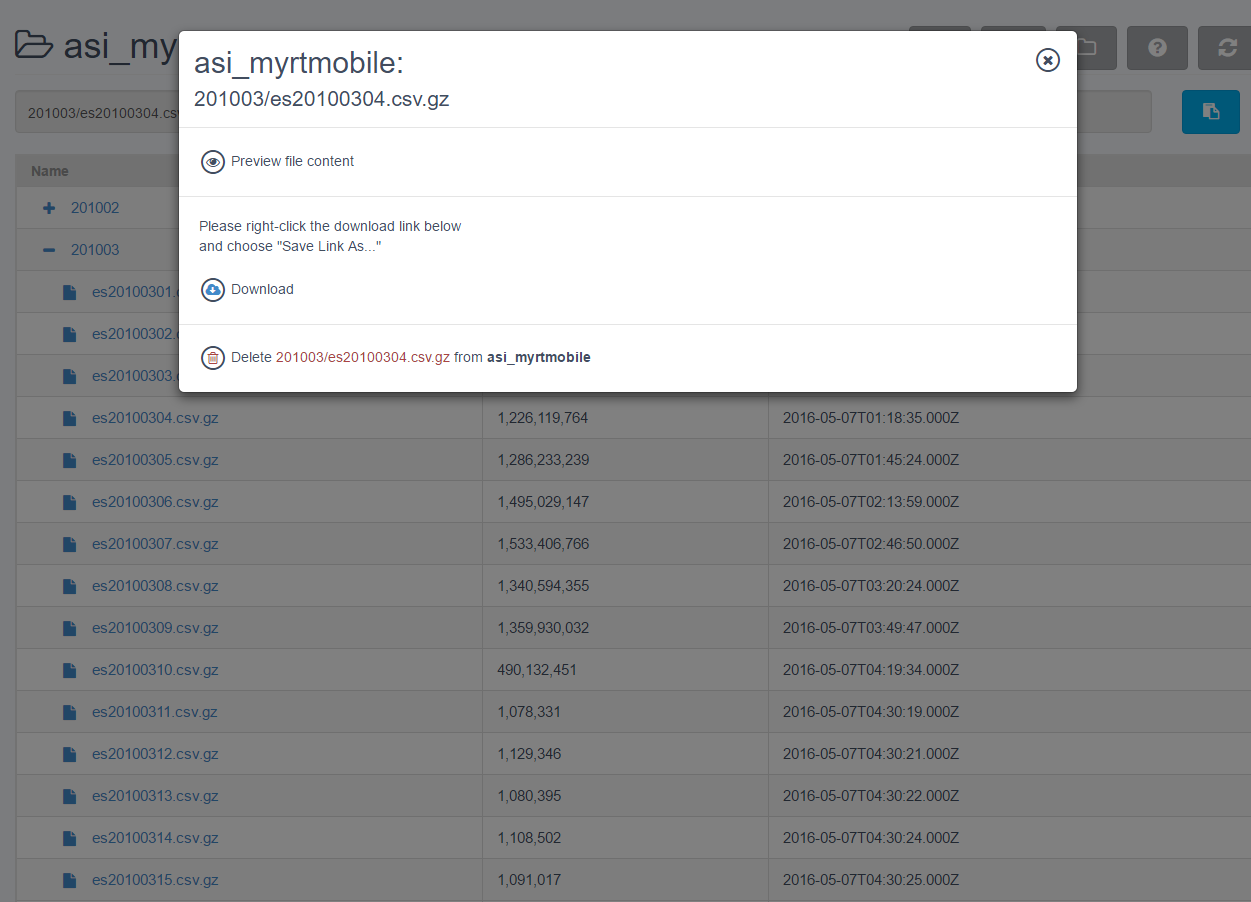
Exploring Your Data Repository
- Click the folder icon next to your respository in the Connect or Categorize tabs of the UI. A new tab will open, allowing you to explore your Data Repository.
- In the new tab, click the + next to a directory to navigate through the directories on your Repository.
- Your current path is displayed at the top, under your repository name. This is useful when defining a pattern for the files you want to group into a category. You can click the blue icon to the right of the displayed path to copy that path to your clipboard.
- You can click the icon next to any filename to Download or Delete that file from your Repository. You can also click the icon and then Preview file content to view an uncompressed sample of the raw data in the file.
Note: If the Explorer tab does not open, you may need to enable pop-ups from the Essentia UI.
You can click the Search icon to look for files matching a globular pattern within the current path on your Repository.
Note: For a more detailed description of globular matching patterns, see Glob (programming)
You can click the Download icon to choose files or folders to download from the current path on your Repository.
You can click the Upload icon to choose files to upload to the current path on your Repository.
You can click the Folder icon to create a new folder in the current path on your Repository.
You can click the Information icon to calculate the total number of files and bytes in the current path on your Repository.
You can click the Refresh icon to get the latest list of files on your Repository.
Datastore category setup and management
Video Demo 1
Video Demo 2
Create category
- Click on Categorize in the top menu and select a Repository from the drop down.
- Click on the + icon to open the input form.
- Define your Category by entering:
- Category Name - any arbitrary name (no spaces).
- Pattern - globular matching pattern(s) to describe what types of files to include in your category.
- Optionally define any number of the following options to speed up data scanning or make data management easier:
- Comment - any arbitrary comment.
- Exclude - globular matching pattern to describe what files to not include in your category. Note: this further restricts the files included by your
Pattern.
- Use cached file list - reference the local file list for the current category instead of accessing the repository.
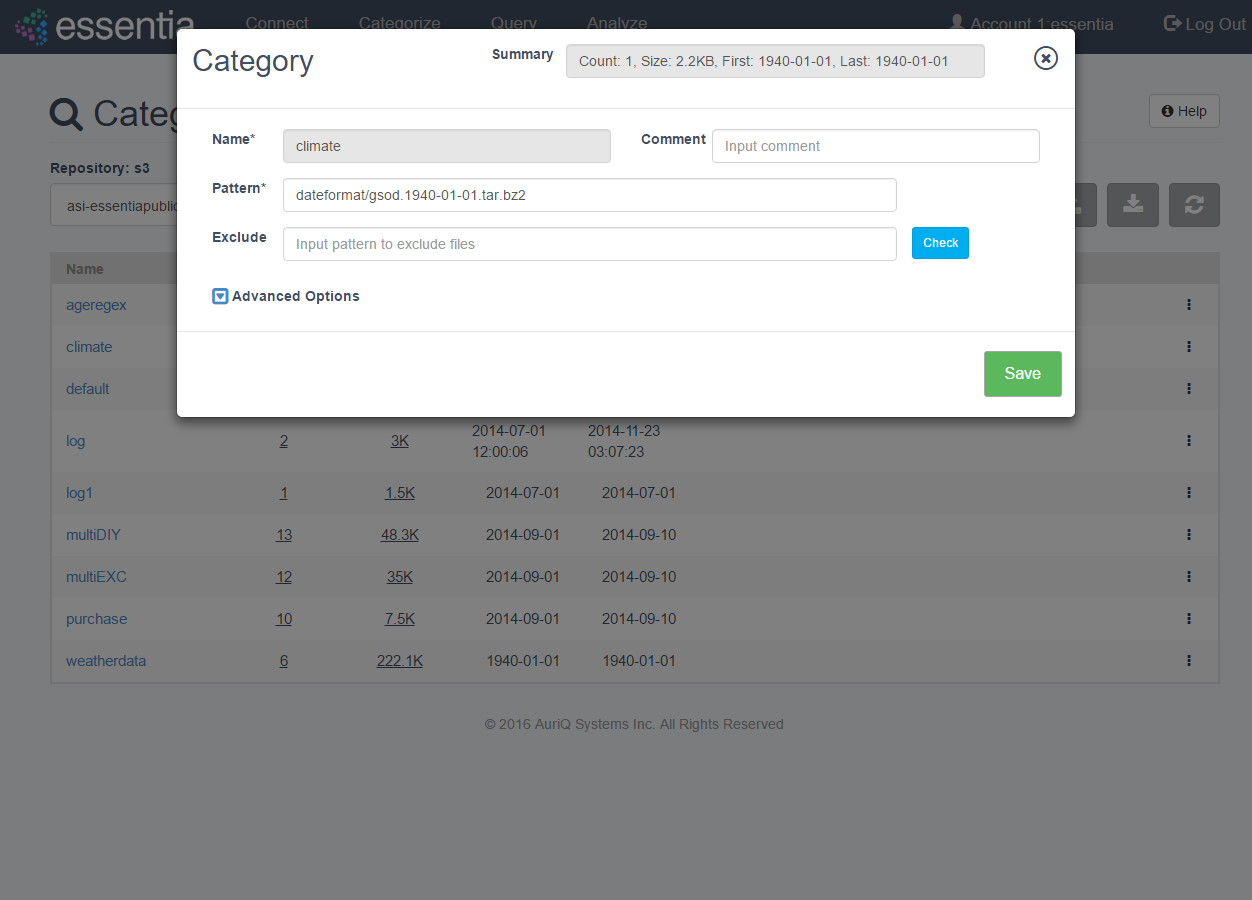
- Or click on the Advanced Options drop down arrow to display additional category options and define either or both of the following options:
- Date Format - matching date extraction pattern found in filename structure. Specify a regular expression pattern to extract the date from your file path/name, see Date Regex.
- Delimiter - the type of delimiter (comma, space, tab, etc) used in your data.
- Click on the Save button to create your category. This may take a few minutes while Essentia scans your data.
- After the scan is complete, the derived column specifications will be displayed along with metadata about your files. Also, you can now choose to do any of the following:
- Define a Preprocess Command
- Select a Pattern for Internal Files within Archive Files
- Directly Edit Column Specification
- Your newly added category will be displayed in the category table for the selected repository. From here you can edit, copy, scan, or delete a category, view a sample of the data or see the list of files that make up your category.
Define a Preprocess Command
- Follow steps 1-6 of creating a category.
- Click on the Advanced Options drop down and enter a Preprocess Command next to Preprocess. You can then Check or save this command to preprocess your data:
- Preprocess - command to modify your raw data before it is scanned by Essentia.
Select a Pattern for Internal Files within Archive Files
- Follow steps 1-6 of creating a category.
- Click on the Advanced Options drop down and enter a pattern next to Archive.
- Archive - matching pattern to describe filenames within a compressed or uncompressed archive file.
Directly Edit Column Specification
- Follow steps 1-6 of creating a category.
- Choose the table or text display icon on the far right of Column Spec Details to display the determined Column Specifcation in your chosen format.
- From here, you can change column headers (no spaces) and assign data types in case the scan was not correct.
- Click on the Save button to save your changes.
In the main Categorize tab of the UI you can also click the download symbol to the right of the search box
to save all of your categories for a single Repository to an Essentia settings file.
Similarly, you can click the upload symbol to the right of the search box
to read in all of your categories for a single Repository from an Essentia settings file.
This makes sharing your categories with other people easy and makes your work easily transferable between computers.
Caution
Uploading an Essentia settings file for a data repository to your instance will overwrite any existing categories you have defined for that repository.
If new files have been uploaded to your repository recently, you should click Refresh to update all of the summary information shown for your categories in the Categorize tab of the UI.
Whenever you use a category for analysis, however, that category always refreshes itself to ensure that your analysis uses the most accurate view of the files in your Repository.
The Refresh button in the Categorize tab is only needed to update the displayed summary information.
By clicking the number in the File Count column of your category, you can view a graph displaying the Daily Trend of File Count.
You can also click the number in the Total Size column to view a graph showing the Daily Trend of File Size for that category.
These graphs can be very useful in tracking the day-to-day changes to your category.
In particular, File Size is an important metric since as the File Size increases for a category, your analyses using that category may require instances with more resources (cpu, memory, disk space, ...).
By clicking the icon in the right-most column of the category table, you can access additional options to gain information about or manage each category:
- List Files: View a list of the files currently matched by your category pattern.
- Sample: View a sample of the raw data in the category.
- Scan: Run a deep scan of the category to determine detailed information such as type and number of unique elements for each column in that category’s data.
- Download Files: Save up to 1GB of files from your category onto your local computer.
- Copy: Create a new category from your existing category. The new category will need to be named and will use the same file pattern and column specification as the original category by default.
- Export: Save your category defintion for your Repository to an Essentia settings file. This file can then be shared with others or imported to other computers you use to load your category definition.
- Remove: Remove your category definition. This step cannot be undone!
Query setup and management
Video Demo
Create a Query
- Click on Query in the top menu and and select a Repository from the drop down
- Enter your SQL like query in the Input your query here area. You can optionally enter a comment for this query so you can reference it later.
- Click on the Run button to view your query results on your screen and then optionally download your query results into a file on your computer by clicking Download and entering a filename.
- If you do not need the results of your query anymore, you can click Clear to delete those results.
- From this point you can access a Saved Query or run a new query. Running another query will clear the previous query’s results.
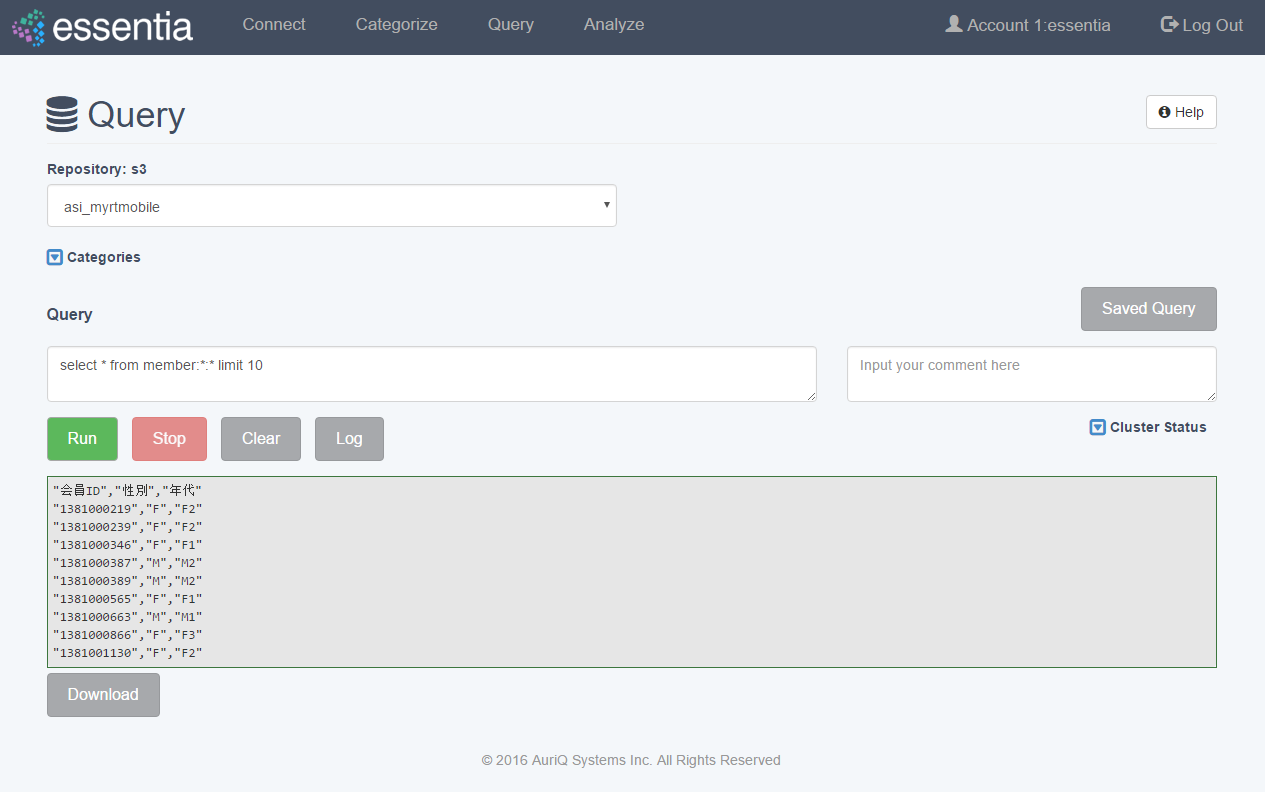
You can view the last 1000 lines of the essentia log file (where debug information, warnings, and errors are written) by clicking Log. This can be useful to determine how you can improve your query.
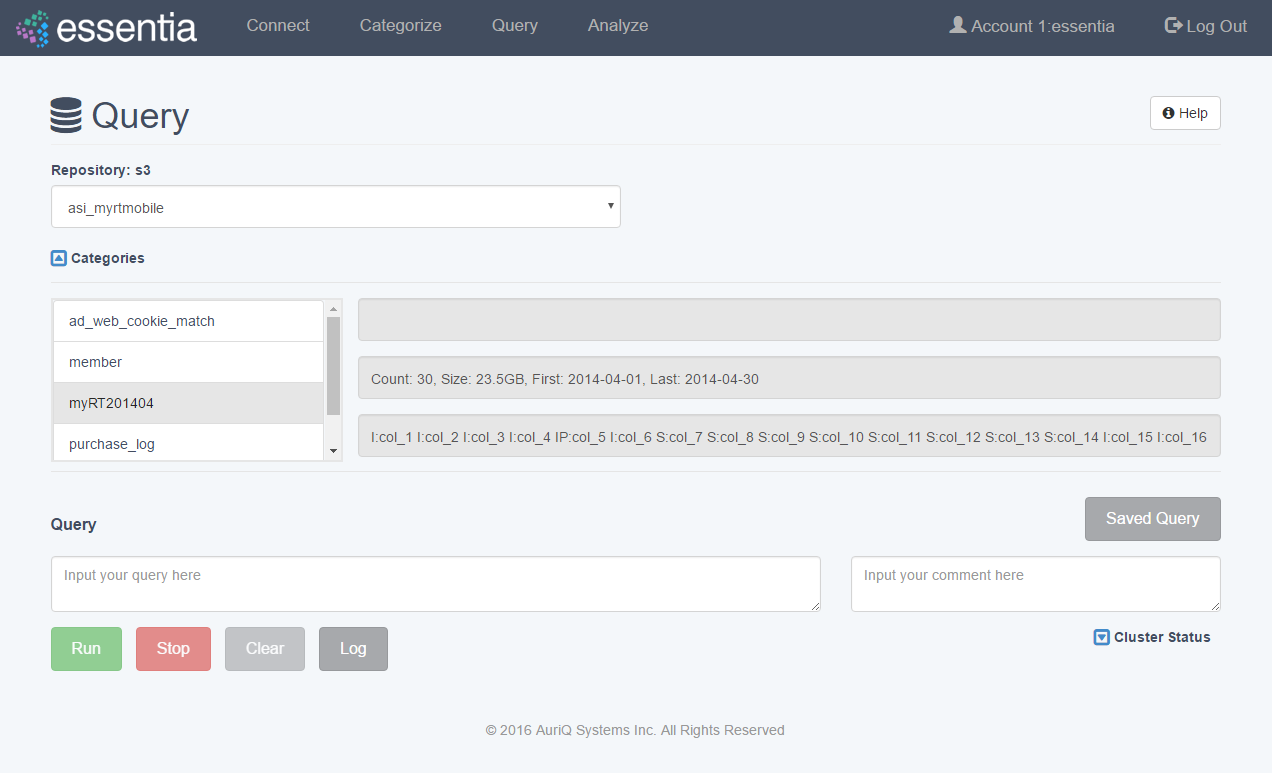
You can click Cluster Status to view status information and resource usage of each of the computers in your cluster. If you are running in local mode on a single computer, you will only see the information for that computer.
Note: If you need to view available categories, click on the Categories drop down arrow to view a list of available categories.
Query Format
select [column_name] | [*] from [category_name]:[start_date | *]:[end_date | *] where ... order by ... limit ...
select count(distinct [column_name] | [*]) from [category_name]:[start_date | *]:[end_date | *] where ...
select [column_name], count(*) from [category_name]:[start_date | *]:[end_date | *] where ... group by [column_name]
Rules
The first query format above is a "select" query.
The second and third query formats above are "count" queries.
1. Group By is NOT supported for SELECT queries.
2. Order By is NOT supported for COUNT queries.
3. Limit is NOT supported for COUNT queries.
4. Group By can only be used when there is no DISTINCT in COUNT queries.
Example
select * from myfavoritedata:*:* where payment >= 50
select * from purchase:2014-09-01:2014-09-15 where articleID>=46 limit 10
To see more examples of the types of queries we allow and work with some sample queries of our public data, please go through our Query Examples
Working with Saved Queries
- Select your Saved Query from the dropdown after clicking the Saved Query button. The query should appear in the “Input your query here” area. If you labeled your query, the label should appear in the box under the Saved Query button.
- Now you can click the Run button to view your query results on your screen and then optionally download your query results into a file on your computer by clicking Download and entering a filename.
You can search your saved queries by clicking on the Saved Query button and entering any parts of your desired queries or labels into the “Search for ...” box.
Script setup and management
Run a Script
- Click on Analyze in the top menu.
- Select a Github Repository from the drop down menu or use the Default (DirectScipt - auriq).
- Enter your Essentia or unix shell commands in the Input your script here area. You can optionally select one of the files from your Github Repository to edit or run. To do this, click the file icon to the left of the filename.
- Click on the Run button to view your script’s results on your screen.
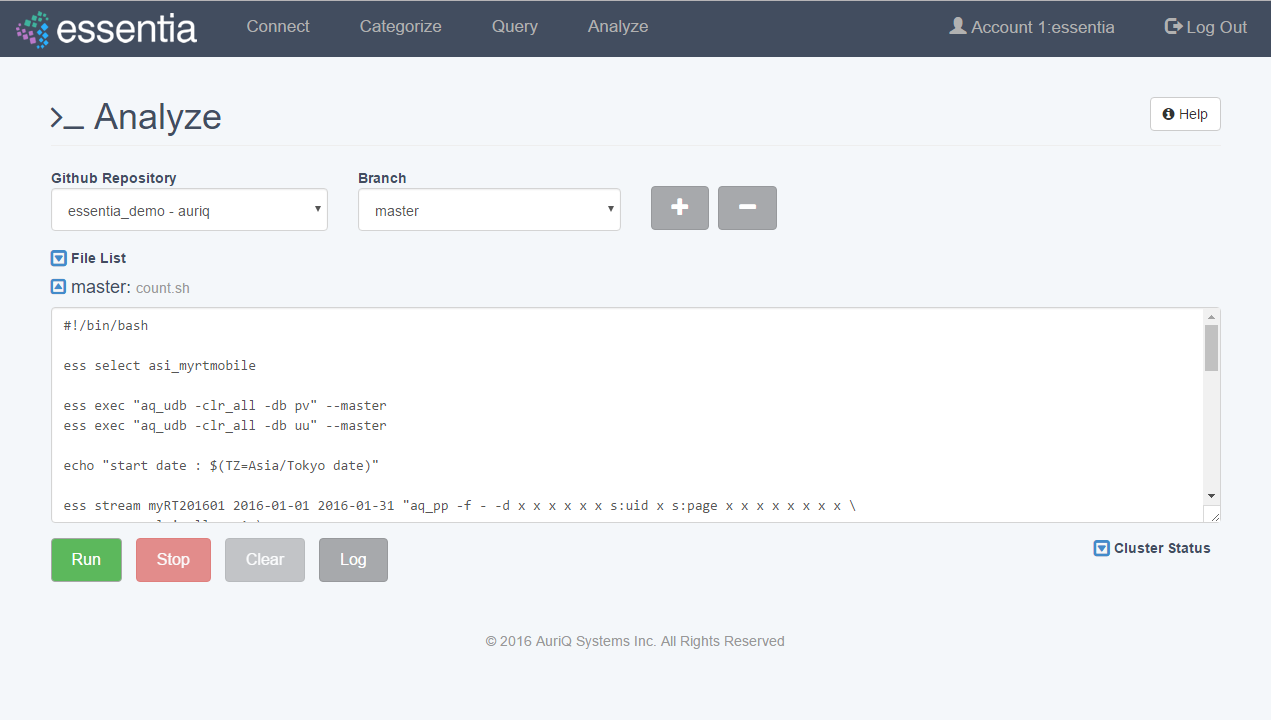
Note: You can also Stop running your script or, when it has finished, Download the result onto your local machine or Clear the results so they are no longer stored. You must terminate any worker cluster before running Clear or you will have to terminate those nodes manually (without Essentia).
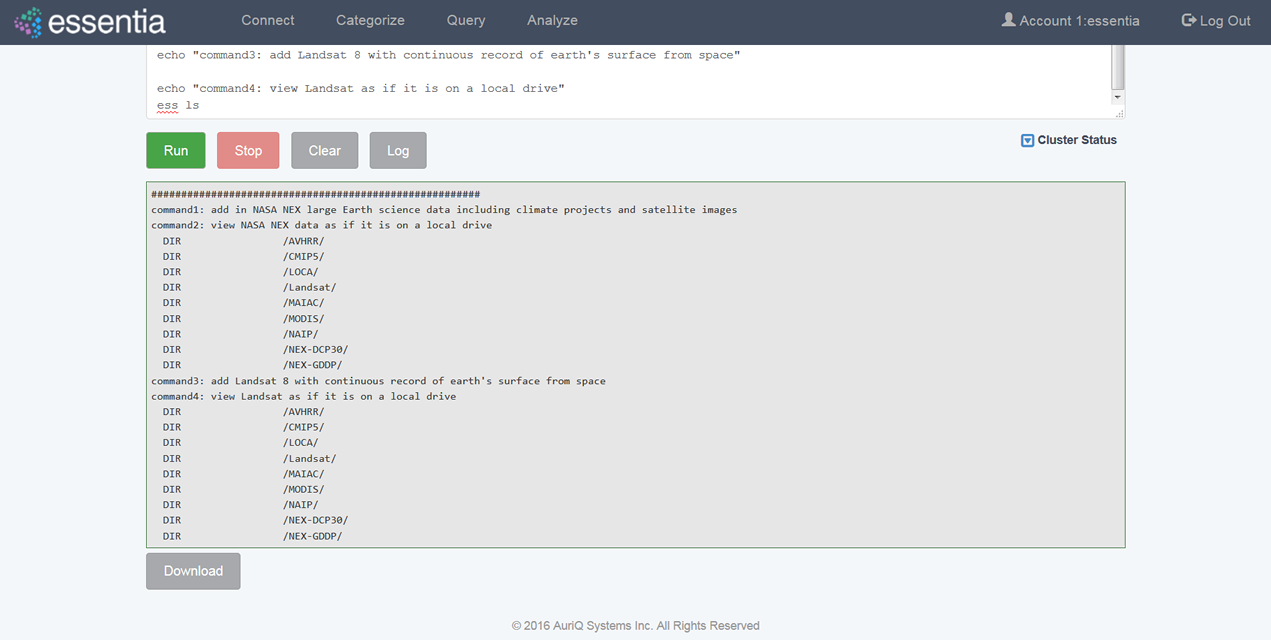
You can view the last 1000 lines of the essentia log file (where debug information, warnings, and errors are written) by clicking Log. This can be useful to determine how you can improve your scripts.
Note: You can also view the status of your master computer and any other machines you are utilizing by clicking on Cluster Status. This will show you the connection information and resource usage of each connected machine.
Connect to a Github Repository
- Click on Analyze in the top menu.
- Click the + button.
- Enter the Owner of your Github Repository, the name of your Repository, and your Personal Access Token. If you do not have a Personal Access Token, follow the instructions found here.
- Click on the Save button to finish adding your Github Repository.
- From this point you can view, edit, and run any of the scripts stored in the Github Repository.
Note: To view or switch between available Github Repositories or Branches, click on the Github Repository or Branch drop down menus.
Questions
Our tutorials are intended to guide you through the usage of the included tools, but you should feel free to contact us at essentia@auriq.com with any other questions.








